GreenVET pathway
| ← close |
 |  |  | ||
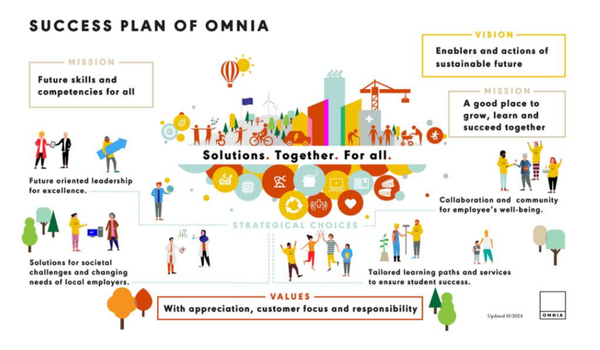
Annual Sustainability Report
Numerous European institutions are setting notable examples in sustainability reporting within the Vocational Education and Training (VET) sector. These reports frequently showcase initiatives aimed at embedding green skills, advancing circular economy practices, and strengthening partnerships with industry and local communities. Key efforts include incorporating environmental sustainability into curricula, fostering business-education collaboration, and promoting lifelong learning opportunities.Key People and Partners Involved
- School management and teaching staff
- Students
- Local community members and organizations
- External facilitators or moderators
Description of the practice
Annual sustainability reports from Vocational Education and Training (TVET) institutions highlight their expanding role in advancing sustainable development. These reports commonly address environmental, social, economic, and governance dimensions of sustainability. On the environmental front, institutions document actions such as reducing energy use, integrating renewable energy, managing resources efficiently, and embedding sustainability into curricula to prepare students for green jobs. Reports may also showcase eco-friendly campus operations, such as sustainable procurement, green infrastructure, and recycling initiatives. Such measures align with global efforts to mitigate climate change and foster a sustainability mindset among learners.Social sustainability is another central theme, with many institutions emphasizing inclusive access to education for women, marginalized groups, and individuals with disabilities. Reports frequently describe initiatives to support equity - such as scholarships, mentorship programs, and tailored learning accommodations. Additionally, TVET providers increasingly engage with local communities and industries through partnerships that address social needs and strengthen lifelong learning. On the economic front, reports highlight how institutions align programs with labor market demands through industry collaboration, curriculum co-design, and work-based learning opportunities. Financial sustainability is also addressed through revenue diversification strategies and long-term viability planning.
Governance and transparency underpin the credibility of sustainability reporting. Many institutions adopt recognized frameworks - such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or UNESCO’s Greening TVET guidelines - to structure their goals, indicators, and reporting processes. Reports often include key performance metrics, stakeholder engagement strategies, and disclosures on sustainability risks and institutional impact. By sharing these reports, VET institutions affirm their commitment to the UN Sustainable Development Goals - especially SDGs 4, 8, 9, 12, 13, and 17 - and position themselves as key enablers of the green and just transitions.
Where it’s being implemented
This link might not lead to content in English language. Use your browser's translate function or automatic captions to explore this resource.- At Vocational School for Hospitality, Gastronomy, and Food Trades BS03 in Hamburg, Germany, the school developed a climate protection plan based on an environmental audit identifying key areas for reducing CO₂ emissions—such as heating, electricity use, waste management, and food sourcing—and provided practical recommendations, like adjusting thermostats, switching to energy-efficient lighting, and sourcing sustainable food.
https://bs03-hamburg.de/download/klimaschutzplan-bs-03-2024/"tmstv=1752062470
Impact and Results
- Better accountability and transparency: Shows progress on sustainability, builds trust with everyone involved, and helps keep improving
- Smarter, more relevant learning: updated courses with green skills so students are ready for future green jobs and hands-on learning
- Stronger partnerships: More relevance and impact through collaboration with industry, local administration
- Strengthening sustainability mindset: Sustainability as a part of your school"s values, daily operations, and teaching
- Aligning with policies and SDGs: Supporting national green strategies and contribution to the SDGs
Implementation Tips and Insights
- Know your "Why": Be clear on why you're writing the report (show progress, attract partners, or link to SDGs) and tie it to your school's bigger goals.
- Don't reinvent the wheel: Use an existing framework like GRI or UNEVOC's guidelines, and start small - you can always grow later.
- Keep it measurable (and realistic): Pick a few simple indicators, like energy use or curriculum changes, and track them each year.
- Get everyone involved: Bring in students, teachers, industry partners, and the community early so the report feels relevang and shared.
- Make it part of everyday work: Link reporting to your existing planning and reporting systems, and have someone (or a small team) lead it.
Useful Links and Resources
This link might not lead to content in English language. Use your browser's translate function or automatic captions to explore this resource. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a globally recognized, independent non-profit standards organization, founded in 1997, with headquarters in Amsterdam. It provides the world’s most widely used sustainability reporting standards—called the GRI Standards—which help organizations across sectors and sizes report transparently on their economic, environmental, and social impacts.Standards are available in many languages.https://www.globalreporting.org/standards/standards-development/universal-standards/
Published by UNESCO-UNEVOC in 2017, this open-access guide promotes a whole-institution approach to Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) within TVET institutions.
https://unevoc.unesco.org/up/Greening%20technical%20and%20vocational%20education%20and%20training_online.pdf
The SDGs Compass is a collaborative guide developed by the UN Global Compact, Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). Introduced in 2015, it helps organizations strategically align their operations with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)—and measure and manage their impacts accordingly. The compass is available in many languages.
https://unglobalcompact.org/library/3101

